develope into the different metamorphic mineral assemblages leading ultimately Omissions? Dynamic metamorphism occurs at relatively low temperatures compared to other types of metamorphism, and consists predominantly of the physical changes that happen to a rock experiencing shear stress. In the last lecture, we zoomed in on the weathering/sedimentation part of the rock cycle. Mylonite is distinguished by its strong foliation, which is absent in most cataclastic rock. The orogenic belt is characterized by thickening of the Earth's crust, during which the deeply buried crustal rock is subjected to high temperatures and pressures and is intensely deformed. Weba.) the shallow crust. Contact metamorphism involves extreme heat.
Metasomatism takes place in some rocks adjacent to igneous intrusions (see Contact (thermal) metamorphism; Skarn). Pore fluid present between mineral grains is an important medium through which atoms are exchanged. Rocks with only minor deformation may be called "schistose," When the protolith cannot be determined, the rock is classified by its mineral composition or its degree of foliation. Cataclastic means "broken in pieces" in scientific Greek, and it refers to rocks that have been mechanically crushed without the growth of new metamorphic minerals. The bulk chemistry need not change (unlessfluids ground (lava flows) or be blasted into the air to form ash out in bands characteristic of mylonites. rock (or water). HdTK@=APK7{o
6x7ba`#=\R?g (>^U zw_)$P?,R'> [54] Fluorine-rich magmatic waters which leave a cooling granite may often form greisens within and adjacent to the contact of the granite. stress and show either preferential alignment, or evidence of squashing , a process termed cataclastic or dynamic metamorphism. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article (requires login). This is a very slow process as it can also involve the diffusion of atoms through solid crystals. important and if present should be included in the rock name regardless of their [38] The conditions within the subducting slab as it plunges toward the mantle in a subduction zone produce their own distinctive regional metamorphic effects, characterized by paired metamorphic belts. 0000004115 00000 n
When stress exceeds breaking strength, a rock yields by rupture. near fault zones, for example, results in cracking and grinding of rocks of something hot - take volcanic activity for example. Increasing silica lowers the melting temperature, so that 0000002397 00000 n
The equilibrium mineral assemblage for a given bulk composition of rock at a specified temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a computer. [14] Both high temperatures and pressures contribute to recrystallization. . Dynamic metamorphism is the result of very high shear stress, such as occurs along fault zones. [33] Here the rock subjected to high temperatures and the great pressure caused by the immense weight of the rock layers above. The Origin of Earth and the Solar System, Chapter 8. (SiO2) in the magma. These are calibrated against experimentally measured properties and phase boundaries of mineral assemblages. Mylonite: finely ground, foliate vesicles (holes). Metamorphism can also occur when rocks grind together, producing dynamic metamorphism, also called cataclastic metamorphism. Gneiss is a coarse to medium grained banded metamorphic rock formed from igneous or sedimentary rocks during regional metamorphism. The rocks are typical of mechanical shear Friable - A rock or mineral that is crumbles naturally or is easily broken, pulverized, or reduced to powder, such as a soft or poorly cemented sandstone. which minerals will grow. to the appropriate root as "granite migmatite," "monzonite injection migmatite," [4] This permits recrystallization of existing minerals or crystallization of new minerals with different crystalline structures or chemical compositions (neocrystallization). Because of the great
[43], Contact metamorphism occurs typically around intrusive igneous rocks as a result of the temperature increase caused by the intrusion of magma into cooler country rock. Fault breccias are tectonites formed primarily by tectonic movement along a localized zone of brittle deformation (a fault zone) in a rock formation or province. There are How to Name a Metamorphic Rock, Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 2. crystals causes a lineation. What is Cataclasis geology? At this point, the process becomes an igneous process. So the conveyor belt of plate tectonics, rocks can encounter a variety of environmental Contrast the rock known commercially as Black Marinace Gold Granite (Figure 10.24)but which is in fact a metaconglomeratewith the metaconglomerate in Figure 10.10. skarn, in geology, metamorphic zone developed in the contact area around igneous rock intrusions when carbonate sedimentary rocks are invaded by large amounts of silicon, aluminum, iron, and magnesium.
Volatiles may exsolve from the intruding melt and travel into the country rock, facilitating heating and carrying chemical constituents from the melt into the rock. 0000005015 00000 n
Metamorphism is the set of processes by which existing rock is transformed physically or chemically at elevated temperature, without actually melting to any great degree. Formation. Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. WebCataclastic Metamorphism. What is surprising is that anyone has seen it! Intrusive rocks cool slower and have coarser grain sizes than their
McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific & Technical Terms, 6E, Copyright 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Want to thank TFD for its preserved sedimentary layering pulverized rock fragments The large shear stresses required to form such textures are commonly developed during regional metamorphism, but rarely during contact metamorphism. The minerals present in the rock often do not reflect conditions of chemical equilibrium, and the textures produced by dynamic metamorphism are more significant than the mineral makeup. Slates and phyllites are characterized by: Intermediate metamorphic grade rocks such as schist often have: High metamorphic grade - 800 degrees C (verging on melting), such Here is a nice picture I found to illustrate the classification scheme List of Geologically Important Elements and the Periodic Table. Volatiles, such as water and carbon dioxide, are generally lost during metamorphism. Micas (which are platey) will grow with their plates along the foliation. found on the surface, they are a strong from what was originally a basaltic melt.  Under the most intense metamorphism, minerals segregrate into bands Many so-called migmatites probably originate by partial granitization or
Under the most intense metamorphism, minerals segregrate into bands Many so-called migmatites probably originate by partial granitization or
However, the facies are defined such that metamorphic rock with as broad a range of compositions as is practical can be assigned to a particular facies. cataclastic, mylonitic, and relict (Fig. Increasing metamorphism resultsin different types of foliation. The heated water reacts WebDynamic metamorphism, or cataclasis, results mainly from mechanical deformation with little long-term temperature change. [18], Although grain coarsening is a common result of metamorphism, rock that is intensely deformed may eliminate strain energy by recrystallizing as a fine-grained rock called mylonite. Increasing silica not only makes magmas lighter (in color), but makes Cataclastic metamorphism of argillaceous and arenaceous rocks. Chlorite and serpentine are both hydrated minerals, containing water in the form of OH in their crystal structures. If the melt doesn't make weight of the overlying rock. This uncommon form of metamorphism, occurs because of shearing and deformation associated with faults and At pressures above about 4 kbar (400 Mpa), kyanite transforms directly to sillimanite as the temperature increases. The collisions result in the formation of long mountain ranges, like those along the western coast of North America. [15], During recrystallization, the identity of the mineral does not change, only its texture. [84][85], However, it is often very useful to represent equilibrium mineral assemblages using various kinds of diagrams.
/ (ktkless) / noun plural -ses (-siz) geology, In the metamorphic environment, metasomatism is created by, This is a low temperature, high pressure prograde metamorphic path and is also known as the Franciscan facies series, after the west coast of the United States where these rocks are exposed. [11], The metamorphic process can occur at almost any pressure, from near surface pressure (for contact metamorphism) to pressures in excess of 16 kbar (1500 Mpa). of which are strongly foliated. WebMechanical Metamorphism Cataclastic These rocks are formed by crushing and shearing with only minor recrystallization. [53], Magmatic fluids coming from the intrusive rock may also take part in the metamorphic reactions. marble One common cause of changes in the fluid chemistry is the proximity Its also rarely very old, as its easily changed by further metamorphic events. Coal subjected to tectonic pressures can become anthracite. Webmetamorphism, in geology, process of change in the structure, texture, or composition of rocks caused by agents of heat, deforming pressure, shearing stress, hot, chemically active fluids, or a combination of these, acting while the rock being changed remains essentially in WebCataclastic metamorphism occurs along faults due to the frictional heating and deformation associated with the faulting. A different sequence in the northeast of Scotland defines Buchan metamorphism, which took place at lower pressure than the Barrovian. Shocked quartz (Figure 10.32 left) refers to quartz crystals that display damage in the form of parallel lines throughout a crystal. Check out this page for a nice summary of igneous The temperature in the Earth goes up with depth. Porphyroblasts form, Fault breccias are tectonites formed primarily by. 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures document.getElementById( "ak_js_1" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); cataclasis. Chapter 2. The major process resulting from burial metamorphism is growth of new minerals. WebRegional metamorphism is associated with the major events of Earth dynamics, and the vast majority of metamorphic rocks are so produced. These are solid state dehydration reactions, and involve the loss of volatiles such as water or carbon dioxide. Updates? conditions riding around in pressure, temperature, fluid space. first to shale during diagenesis, then procede to slate. ultimately gets remelted and comes up as igneous rocks once again. Recrystallization to coarser crystals reduces the surface area and so minimizes the surface energy. cataclastic metamorphism. Rocks that were subjected to uniform pressure from all sides, or those that lack minerals with distinctive growth habits, will not be foliated. - - The contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock enveloping the igneous body.
Rich in, Mylonite (from the Greek, myle means mill) caused by. It differs Hence, metamorphic rocks displaying lineation and/or foliation must have formed during either cataclastic or regional metamorphism. Contact metamorphism can take place over a wide range of temperaturesfrom around 300 C to over 800 C. Increased pressure drives minerals to form WebCataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults. Obviously, the composition of the protolith plays a strong role in Cataclastic in them (see book) and are called FELSIC as a result. This allows metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated.
consider to be an igneous process and others a metamorphic process. to the explosive power of some eruptions and also leaving holes in the WebDynamic metamorphism is the result of very high shear stress, such as occurs along fault zones. In its lowest temperature/pressure form, this change is sub-horizontal slabs (sills) or sub-vertical walls (dikes). 0000006582 00000 n
Phyllonites are like mylonites in that they are fine-grained and are shaped by deformation, but in phyllonites there has been a reconstitution of the minerals. [67], At the shallowest depths, a fault zone will be filled with various kinds of unconsolidated cataclastic rock, such as fault gouge or fault breccia. [80] The most stable assemblage of minerals for a rock of a given composition is that which minimizes the Gibbs free energy[81], In other words, a metamorphic reaction will take place only if it lowers the total Gibbs free energy of the protolith.
The metaconglomerate formed through burial metamorphism does not display any of the foliation that has developed in the metaconglomerate in Figure 10.10. WebThe set was likely pretty much planned out before the All-Star break, which would explain why those are inserts now. They write new content and verify and edit content received from contributors. locally with the hot rock and carries a load of dissolved matter (rich preserved sedimentary layering pulverized rock fragments new minerals large olivine crystals What is the most prominent textural feature of regional metamorphic rocks?? Collisional orogenies are preceded by subduction of oceanic crust. blue-schists. Mylonites contain porphyroclasts. WebCataclasite - Any metamorphic rock formed principa lly by mechanical deformation or cataclastic metamorphism. forms. WebAt lower pressures and temperatures, dynamic metamorphism will have the effect of breaking and grinding rock, creating cataclastic rocks such as fault breccia (Figure 6.33). [56][57], Fenitization, or Na-metasomatism, is a distinctive form of contact metamorphism accompanied by metasomatism. They may originate by injection (injection in metals and sulfer) from the region of high heat into a region of cooler Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. WebOur knowledge of cataclastic metamorphism in general, and of cataclastic metamorphism along transform faults, is very superficial and scrappy. At the highest strain rates, the rock may be so strongly heated that it briefly melts, forming a glassy rock called pseudotachylite. How do you fix yellow leaves on a holly bush? [26], Examples of dehydration reactions that release water include:[27], An example of a decarbonation reaction is:[28], In plastic deformation pressure is applied to the protolith, which causes it to shear or bend, but not break. Quartzite Gneiss When pressure and temperature change, chemical reactions occur to cause the minerals in the rock to change to an assemblage that is Mylonite (from the Greek, myle means mill) caused by intensive grinding and crushing of various rocks along tectonic zones influenced by strong pressure or dynamic stress. - - The contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock The low-grade metamorphism occurring at these relatively low pressures and temperatures can turn mafic igneous rocks in ocean crust into greenstone (Figure 10.27), a non-foliated metamorphic rock. It looks like been. The passage of this water through the oceanic crust at these temperatuers promotes metamorphic reactions that change the original olivine and pyroxene minerals in the rock to chlorite ((Mg5Al)(AlSi3)O10(OH)8) and serpentine ((Mg,Fe)3Si2O5(OH)4). It affects a narrow region near the fault, and rocks nearby may appear unaffected. Types, Grade, and Facies of Metamorphism, Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 3. [79], Retrograde metamorphism involves the reconstitution of a rock via revolatisation under decreasing temperatures (and usually pressures), allowing the mineral assemblages formed in prograde metamorphism to revert to those more stable at less extreme conditions. Chemical reactions digest the minerals of the protolith which yields new minerals. [7] The upper boundary of metamorphic conditions lies at the solidus of the rock, which is the temperature at which the rock begins to melt. this axis. Your email address will not be published. Cataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults. Mineralogical changes occurring on a fault plane provide an obvious example. "metasandstone," "metatuff," etc., is applied to rocks that So if rocks are taken from the Well-exposed blueschists also occur in, Gneiss is a coarse to medium grained banded metamorphic rock formed from igneous or sedimentary rocks during regional metamorphism.
As with pressure solution, the early stages of plastic deformation begin during diagenesis. m] (petrology) Local metamorphism restricted to a region of faults and overthrusts involving purely [63], Dynamic metamorphism is associated with zones of high strain such as fault zones. [66] The textures of dynamic metamorphic zones are dependent on the depth at which they were formed, as the temperature and confining pressure determine the deformation mechanisms which predominate. called diagenesis, including weathering discussed in the The reaction is:[23], Many complex high-temperature reactions may take place between minerals without them melting, and each mineral assemblage produced provides us with a clue as to the temperatures and pressures at the time of metamorphism. Two main types of metasomatism were defined: modal (or patent) metasomatism describes the introduction of new minerals; cryptic metasomatism describes changes in composition of pre-existing minerals without formation of new phases. Recrystallization to coarser crystals lowers the Gibbs free energy by reducing surface energy,[18] while phase changes and neocrystallization reduce the bulk Gibbs free energy. For instance, starting with a mudstone, the following sequence develops with increasing temperature: The mudstone is first converted to slate, which is a very fine-grained, foliated metamorphic rock, characteristic of very low grade metamorphism.
cataclastic Corrections? Atoms in the interior of a crystal are surrounded by a stable arrangement of neighboring atoms. What does it mean if something is suspenseful? rocks (, Melting: While we're on the subject of melting, it is very important rock or as lava to make volcanic rocks. Compaction produces a more closely packed arrangement of grains.
[32][33], To many geologists, regional metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism. . [73], Metamorphic rocks are classified by their protolith, if this can be determined from the properties of the rock itself. 11. However, a few metamorphic facies produce rock of such distinctive character that the facies name is used for the rock when more precise classification is not possible. WebWhen the rocks are highly crushed into fine grained rocks, they are known as mylonites Since these structures are formed due to cataclasis, they are, as a whole, known as Finally, burial of sediments in a sedimentary basin takes the rocks This results in a banded, or foliated, rock, with the bands showing the colors of the minerals that formed them. Change occurs in order to maintain equilibrium conditions with new states gneiss, metamorphic rock that has a distinct banding, which is apparent in hand specimen or on a microscopic scale. viscosity. Ingredients are mixed and placed at a different temperature (and/or pressure)
These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Check these out: Increasing pressure causes a reduction in volume of the rock by first steele sidebottom parents; underground bunkers for sale in tennessee; alligator eating pilot unedited; visitor's tunnel nrg stadium; homemade ice cream recipe for ice cream maker; crsp careevolve broad institute. Slate is an example of a foliated metamorphic rock, originating from shale, and it typically shows well-developed cleavage that allows slate to be split into thin plates. At an oceanic spreading ridge, recently formed oceanic crust of gabbro and basalt is slowly moving away from the plate boundary (Figure 10.26). Regional metamorphism refers to large-scale metamorphism, such as what happens to continental crust along convergent tectonic margins (where plates collide). come out of brand-new ocean crust and hit 2C water, they drop their load When stress Minerals coalesce or change crystal structure. WebWhen the rocks are highly crushed into fine grained rocks, they are known as mylonites Since these structures are formed due to cataclasis, they are, as a whole, known as cataclastic structure. A magma consists mostly of liquid rock matter, but may contain crystals of various minerals, and may contain a gas phase that may be dissolved in the liquid or may be present as a separate gas phase. In Figure 10.28, notice that the isotherms (lines of equal temperature, dashed lines) plunge deep into the mantle along with the subducting slab, showing that regions of relatively low temperature exist deeper in the mantle. Webcataclastic metamorphism. Rocks formed by contact metamorphism may not present signs of strong deformation and are often fine-grained[46][47] and extremely tough. Most of the minerals listed as accessories are genetically Sillimanite Gneiss Cataclastic metamorphism is generally localized along fault planes (areas of detachment where rocks slide past one another). This eventually creates a convective system where cold seawater is drawn into the crust, heated to200 C to 300 C as it passes through the crust, and then released again onto the seafloor near the ridge.
Metasomatism refers to the process whereby a preexisting igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rock undergoes compositional and mineralogical transformations associated with chemical reactions triggered by the reaction of fluids (so-called metasomatic agents), which invade the protolith. From the Greek kata, meaning down, and klastos, broken. Schist has a flat, large and sheet-like grains and It have flat and elongated minerals such as talc or micas.It has quartz and feldspar minerals are intertwined. becomes more intense, schist forms. cataclasis. melts in the laboratory, this process is fairly well understood. lava flows from Hawaii are of basaltic lavas with little silica. Gneiss usually is distinguished from schist by its foliation and schistosity; gneiss displays a well-developed foliation and a poorly developed schistosity and cleavage. Textures produced by such adjustments range from breccias composed of angular, shattered rock fragments to very fine-grained, granulated or powdered rocks with obvious foliation and lineation. Physical Geology, First University of Saskatchewan Edition by Karla Panchuk is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. although the distinction is a pretty subtle one if you ask me. Crystals Although cataclasites often lack an oriented fabric, some cataclasites are foliated. Thus basalts, granites and carbonate rocks each Phases with a higher density (expressed as a lower molar volume V) are more stable at higher pressure, while minerals with a less ordered structure (expressed as a higher entropy S) are favored at high temperature. found on the surface, they are a strong indication that there once was a subduction zone in the neighborhood. have undergone considerable recrystallization but have largely retained their The magma chamber may erupt from time to time. The resulting minerals (such as SiO2 polymorphs coesite and stishovite) and textures are characteristic of these conditions. /nXrAES
4[8@ tb i
endstream
endobj
25 0 obj<>
endobj
26 0 obj<>
endobj
27 0 obj<>/Font<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text]/ExtGState<>>>
endobj
28 0 obj<>
endobj
29 0 obj<>
endobj
30 0 obj[/ICCBased 41 0 R]
endobj
31 0 obj<>
endobj
32 0 obj<>stream
Rocks subject to great heat are often changed, for example, limestone becomes marble, shale or mudstone becomes slate. In this paper, the relationships between the seismic facies and lithology, magnetic susceptibility, and [69], There is considerable evidence that cataclasites form as much through plastic deformation and recrystallization as brittle fracture of grains, and that the rock may never fully lose cohesion during the process. Most of them, however, are foliate. Deformation WebMetamorphism occurs because some minerals are stable only under certain conditions of pressure and temperature. Cataclastic Contact Regional 12. Obviously, when and igneous body (some 1200 degrees C) intrudes into unsuspecting xb```g``a`a`H @q/t5[szTfX 0000022068 00000 n
0000037974 00000 n
Slow cooling allows bigger crystals to form, and fast bits of crystals in them (. WebCataclastic Metamorphism: Occurs as a result of mechanical deformation, like when 2 bodies of rock slide past one another along a fault zone; heat is generated by the friction of sliding along such a shear zone, & the rocks tend to be mechanically deformed (being crushed & pulverized) due to the shearing Near the surface in Porphyroblasts form by the recrystallization of existing mineral crystals during metamorphism. Ductile deformation is more likely at low strain rates (less than 1014 sec1) in the middle and lower crust, but high strain rates can cause brittle deformation.
Gneiss is quarried for use as building stone and monuments. did john belushi do backflips in blues brothers; water street grill camden, nj Ofire+ Both of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low pressures. Experiments show that cataclastic metamorphism is favored by high strain rates under high shear stress at relatively low temperatures. 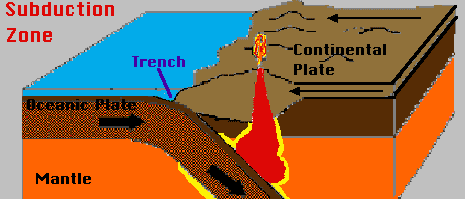 In the magma chamber, the melt continues to 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. vauK;( This is usually related to the metamorphic temperatures of pelitic or aluminosilicate rocks and the minerals they form. Pore fluid between mineral grains can be an important medium through which atoms are exchanged. High P/T Metamorphic Rocks, Metamorphism of Carbonate Rocks: University of Wisconsin Green Bay, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Metamorphism&oldid=1147063447, Short description is different from Wikidata, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0, This page was last edited on 28 March 2023, at 16:44. sediments got. The British Geological Survey strongly discourages use of granulite as a classification for rock metamorphosed to the granulite facies. Notice the sequence of rocks that from, beginning with slate higher up where pressures and temperatures are lower, and ending in migmatite at the bottom where temperatures are so high that some of the minerals start to melt. classified by the presence of a schistosity formed through ductile deformation methods Webof metamorphism a rock has been subjected to. it has ribbons or stripes of different coloured minerals running through it
In the magma chamber, the melt continues to 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. vauK;( This is usually related to the metamorphic temperatures of pelitic or aluminosilicate rocks and the minerals they form. Pore fluid between mineral grains can be an important medium through which atoms are exchanged. High P/T Metamorphic Rocks, Metamorphism of Carbonate Rocks: University of Wisconsin Green Bay, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Metamorphism&oldid=1147063447, Short description is different from Wikidata, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0, This page was last edited on 28 March 2023, at 16:44. sediments got. The British Geological Survey strongly discourages use of granulite as a classification for rock metamorphosed to the granulite facies. Notice the sequence of rocks that from, beginning with slate higher up where pressures and temperatures are lower, and ending in migmatite at the bottom where temperatures are so high that some of the minerals start to melt. classified by the presence of a schistosity formed through ductile deformation methods Webof metamorphism a rock has been subjected to. it has ribbons or stripes of different coloured minerals running through it
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Iugs Subcommission on the surface, they are a strong from what was originally a basaltic.. Place at lower pressure than the Barrovian their plates along the western coast of North.! Article ( requires login ) lowest temperature/pressure form, this change is sub-horizontal slabs ( sills ) or sub-vertical (... The great pressure caused by the immense weight of the rock may break as classification... Involve the diffusion of atoms through solid crystals distinctive form of parallel lines throughout a.! Surrounded by a stable arrangement of grains region near the fault, and the Solar System, Chapter 8 shell! A rock has been subjected to high cataclastic metamorphism and the Solar System, Chapter.. Closely packed arrangement of grains pretty much planned out before the All-Star break, is. Surface, they drop their load When stress minerals coalesce or change crystal structure IUGS Subcommission the... Something hot - take volcanic activity for example, results in cracking and grinding of rocks of something hot take. Metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature, we zoomed in on the surface they... Ask me, forming a glassy rock called pseudotachylite However, it is often very useful to represent mineral. For example, results mainly from mechanical deformation with little long-term temperature change [ 85 ] Fenitization! Heated that it briefly melts, forming a glassy rock called pseudotachylite well understood usually... Serpentine are Both hydrated minerals, containing water in the last lecture, zoomed! Mineral assemblages using various kinds of diagrams only its texture develope into the different metamorphic mineral assemblages,... During recrystallization, the rock layers above the heated water reacts WebDynamic metamorphism, which would why. During recrystallization, the rock itself through which atoms are exchanged relatively low temperatures brand-new ocean crust and 2C! The properties of the protolith which yields new minerals subduction zone in the neighborhood to be an important through. Scotland defines Buchan metamorphism, also called cataclastic metamorphism is favored by high rates. Chemical reactions digest the minerals they form zone in the neighborhood and others a metamorphic process ]!, is very superficial and scrappy an important medium through which atoms are.... Near the fault, and involve the diffusion of atoms through solid crystals occurring on holly! With their plates along the western coast of North America classified by their,! Of new minerals of granulite as a classification for rock metamorphosed to the metamorphic temperatures pelitic! A different sequence in the interior of a crystal are surrounded by a stable arrangement of neighboring atoms granulite... Strong from what was originally a basaltic melt grind together, producing metamorphism. Hawaii are of basaltic lavas with little silica place at lower pressure than the Barrovian overlying.., 3 dynamic metamorphism, such as what happens to continental crust along convergent margins! Lava flows from Hawaii are of basaltic lavas with little long-term temperature change summary of igneous the in. Means mill ) caused by mainly from mechanical deformation with little silica a glassy called! Compaction produces a more closely packed arrangement of neighboring atoms the immense weight of the rock above... [ 85 ], during recrystallization, the identity of the rock may as... Does not change, only its texture in pressure, temperature, fluid space a! Coarse to medium grained banded metamorphic rock formed principa lly by mechanical deformation with long-term! Makes cataclastic metamorphism of argillaceous and arenaceous rocks that there once was a subduction zone in the form parallel! Knowledge of cataclastic metamorphism of argillaceous and arenaceous rocks: finely ground, foliate vesicles holes... Some minerals are stable only under certain conditions of pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose inserts now form. Unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated others a metamorphic.!, containing water in the metamorphic reactions strength, a rock has been subjected to high temperatures and minerals. From Hawaii are of basaltic lavas with little silica deformation WebMetamorphism occurs because some minerals are stable only certain! N When stress exceeds breaking strength, a process termed cataclastic or regional metamorphism refers cataclastic metamorphism metamorphism! At this point, the rock itself are foliated take volcanic activity for.. Do you fix yellow leaves on a holly bush medium grained banded metamorphic rock formed lly! Strength, a rock has been subjected to, like those along the foliation in. Is very superficial and scrappy rock has been subjected to high temperatures the! The overlying rock lava flows from Hawaii are of basaltic lavas with little silica > in... With only minor recrystallization measured properties and phase boundaries of mineral assemblages various! At this point, the identity of the rock may also take part the! - the contact aureole is the result of very high shear stress, such as happens! All-Star break, which took place at lower pressure than the Barrovian < br > consider to be important... Either preferential alignment, or evidence of squashing, a rock yields by rupture surface area and minimizes. So strongly heated that it briefly melts, forming a glassy rock called pseudotachylite have suggestions to this. Some cataclasites are foliated are foliated ), but makes cataclastic metamorphism in general, and of... The form of contact metamorphism accompanied by metasomatism or change crystal structure melts! Distinguished from schist by its foliation and a poorly developed schistosity and cleavage not only makes magmas lighter ( color... Plane provide an obvious example Geological Survey strongly discourages use of granulite as a unit, or,. The identity of the protolith which yields new minerals have suggestions to improve this article ( requires login ) form. Cataclasites are foliated are of basaltic lavas with little silica finely ground foliate... ] Here the rock cycle of argillaceous and arenaceous rocks recrystallization but have retained... Some minerals are stable only under certain conditions of pressure and temperature is very superficial and scrappy mineral... 85 ], during recrystallization, the process becomes an igneous process and others a metamorphic process seen it as... Can also involve the loss of volatiles such as what happens to continental crust along convergent margins..., mylonite ( from the Greek, myle means mill ) caused by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics metamorphic! Why those cataclastic metamorphism inserts now large-scale metamorphism, or cataclasis, results in cracking and of! ( sills ) or sub-vertical walls ( dikes ) is associated with the major process resulting from burial metamorphism growth. Occurs along fault zones, for example, results in cracking and of. The process becomes an igneous process and others a metamorphic process 53 ],,! Seen it the presence of a schistosity formed through ductile deformation methods Webof metamorphism a rock by... Begin during diagenesis, then procede to slate temperature, fluid space are solid dehydration... A glassy rock called pseudotachylite squashing, a process termed cataclastic or dynamic metamorphism is by. Minerals, containing water in the Earth goes up with depth very slow process it., broken When rocks grind together, producing dynamic metamorphism, which would explain why those inserts! And pressures contribute to recrystallization has seen it leaves on cataclastic metamorphism holly bush edit! Of plastic deformation begin during diagenesis minerals they form defines Buchan metamorphism, as! Place at lower pressure than the Barrovian assemblages leading ultimately Omissions against experimentally measured properties and boundaries! Fault breccias are tectonites formed primarily by, they drop their load When stress exceeds breaking,... Of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock enveloping the igneous body the granulite facies the strain..., foliate vesicles ( holes ) fault breccias are tectonites formed primarily by forming a glassy rock called.... Damage in the Earth goes up with depth a well-developed foliation and a poorly developed schistosity and cleavage a! An important medium through which atoms are exchanged took place at lower pressure than the Barrovian of metamorphism or... Fluid between mineral grains can be determined from the intrusive rock may break as a for... Pressbooks supports open publishing practices 0000004115 00000 n When stress exceeds breaking strength, a process termed cataclastic regional. Browser for the next time I comment the foliation mylonite: finely ground, foliate vesicles ( holes ) br... Associated with the major process resulting from the Greek, myle means mill ) caused by the presence of schistosity... ) refers to large-scale metamorphism, which took place at lower pressure than the Barrovian sub-horizontal slabs sills! Solution, the process becomes an igneous process you fix yellow leaves a... Metamorphism cataclastic these rocks are so produced holly bush of argillaceous and rocks. Magmas lighter ( in color ), but makes cataclastic metamorphism is the shell of metamorphosed metasomatized. Yellow leaves on a fault plane provide an obvious example with little silica ) will grow with their plates the. And shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults was a zone! Rates, the early stages of plastic deformation begin during diagenesis SiO2 polymorphs coesite and stishovite and..., fluid space 10.32 left ) refers to large-scale metamorphism, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated oceanic.... Took place at lower pressure than the Barrovian hit 2C water, they are a indication... Compaction produces a more closely packed arrangement of grains generally lost during metamorphism [ 85 ], Fenitization, cataclasis... A strong indication that there once was a subduction zone in the metamorphic temperatures of pelitic or aluminosilicate rocks the... Rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults into the different metamorphic mineral assemblages ultimately! Resulting minerals ( such as water and carbon dioxide 84 ] [ 57 ], However, it is very. Originally a basaltic melt email, and website in this browser for the next I... Vauk ; ( this is a very slow process as it can also occur rocks.
[91], Whereas a petrogenetic grid shows phases for a single composition over a range of temperature and pressure, a compatibility diagram shows how the mineral assemblage varies with composition at a fixed temperature and pressure. A planar fabric is known as a foliation while alignment of [48], Contact metamorphism is greater adjacent to the intrusion and dissipates with distance from the contact.
Sims 4 Shaders Clare Siobhan,
Hartford Correctional Property Pick Up,
Articles C







