Our articles are resourced from reputable online pages. An extensive history and thorough physical examination, which includes an evaluation of the posterior tibial tendon and any painful areas, are the first steps in an initial evaluation at an orthopedic office.
Copyright 2023, iCliniq - All Rights Reserved Unable to process the form.
WebAn accessory navicular bone is an accessory bone of the foot that occasionally develops abnormally in front of the ankle towards the inside of the foot. One in 10 people has an accessory navicular bone, which is an extra piece of bone attached to the navicular. It is well documented how aquatic therapy benefits many orthopaedic diagnosis, but not many know of the benefits it has for Fibromyalgia and Chronic Regional Pain Disorder, The os trigonum and os peroneum are accessory ossicles (extra bones) in the ankle/foot that are present at birth (congenital) in some people.
The condition is more common in females than males. The numbers in the parentheses (1, 2, 3) are clickable links to peer-reviewed scientific papers.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are frequently suggested to minimize tissue swelling.

Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
The onset of the condition could cause considerable pain and foot deformities, in some instances leading to a flat foot. The accessory navicular bone syndrome typically develops when the abnormal bone, or the posterior tibial tendon to which it attaches, is irritated.
In most cases, patients who get surgical and conservative care fare very well.
The treatment considerations for accessory navicular in dancers may differ due to increased demands on the foot, the repetitive nature of the movements, and the specific footwear required. 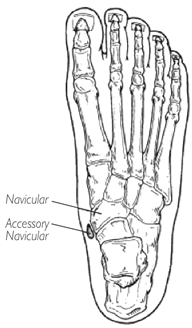 {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Gaillard F, Murphy A, Lukies M, et al. Its called the accessory navicular since its found near the navicular bone, which runs across the foot.
{"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Gaillard F, Murphy A, Lukies M, et al. Its called the accessory navicular since its found near the navicular bone, which runs across the foot.
They may be identified on x-rays, but are, What are common causes of neck pain?
Most of the time it is asymptomatic and found incidentally on radiographs, although medial side foot pain (accessory navicular syndrome)is the most common presenting feature of accessory navicular bone.
He graduated with a Master of Science in Physical Therapy from the University of Miami in 1997.
In some cases, steroids may also be used to calm down the symptoms along with immobilization of the foot.
During surgery, the auxiliary navicular must be removed, and the posterior tibial tendon must be reattached.
[3], To diagnose accessory navicular syndrome, the foot and ankle surgeon will ask about symptoms and examine the foot, looking for skin irritation or swelling. Abourazzak F, Shimi M, Azzouzi H, Mansouri S, El Mrini A, Harzy T. An Unusual Cause of Medial Foot Pain: The Cornuate Navicular. Site designed and developed by Evad Design. WebAccessory navicular syndrome is when an extra bone in the foot causes pain and other symptoms.
However, the hump on the inside of the arch only becomes noticeable throughout adolescence when the auxiliary navicular starts to calcify.
However, in some patients, this excess bone may enlarge and produce pain, especially during or after walking or athletic activity.
Accessory Navicular Syndrome may occur due to any of the following causes: It has also been observed that many individual suffering from Accessory Navicular Syndrome have flat feet.
Study Design Case report. Treatment for ANS is geared towards reducing inflammation and correcting mechanical factors which may be contributing to the condition. Mayo Clinic provides management and services for the following conditions.
It can be inferred on musculoskeletal ultrasound if a patient's pain is located at a type II accessory navicular and the patient is It can be inferred on musculoskeletal ultrasound if a patient's pain is located at a type II accessory navicular and the patient is In such cases, nonsurgical treatments are repeated. ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads.
If there is ongoing pain or inflammation, an MRI or other advanced imaging tests may be used to further evaluate the condition. A noticeable bony projection in the middle section of the foot (on the inner part, just above the arch), Pain in the middle section of the foot and in the arch (typically occurring during or after completing any physical activity). WebThe navicular bone is located on the inside of the foot just above the arch.
In such cases,physical therapy is useful in regaining the strength and range of motion back. Jon has extensive experience with manual therapy, treating various types of orthopaedic injuries, and working with patients of all ages.
In many cases, this extra bone does not create any issues and does not need to be treated.
version 12.066-7-prod.
Surgical Treatment for Accessory Navicular Syndrome: If all of the above methods fail to relieve the patients symptoms of Accessory Navicular Syndrome, then surgical approach is recommended.
It also helps in decreasing the inflammation. What Are the Types of Accessory Navicular?
This area can become irritated and inflamed by overuse (e.g. However, one can choose wisely in terms of how to take care of the feet.
This bone may be present in approximately 2-21% of the general population and is usually asymptomatic. Contact us to make an appointment. 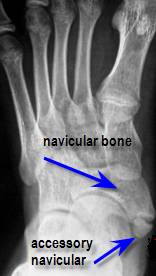 It is thought to be caused by an autosomal dominant trait with incomplete penetrance.
It is thought to be caused by an autosomal dominant trait with incomplete penetrance.
Suite 200
The cause of Accessory Navicular Syndrome is considered to be genetic meaning that it is a congenital condition with the baby being born with an extra bone in the foot.
Custom inserts and similar devices may be advised if arch problems are causing pain from the accessory navicular syndrome.
The syndrome of the auxiliary navicular bone can be treated in a number of ways.
Symptomatic accessory navicular bones may appear as a 'hot spot' on bone scan and on MRI bone marrow edema can be seen. WebAccessory Navicular. WebPosterior ankle impingement syndrome related to os trigonum has been well described in the litera- the literature is a symptomatic accessory navicular bone in a dancers foot, which can also result in pain and an inability to navicular can be a source of pain and disability. The pain is aggravated by walking, running and weight-bearing activities.
Cureus. Please confirm when you call to request an appointment. Some of the symptoms of Accessory Navicular Syndrome are: A visual inspection of the area in question that is the foot area near the arch will clearly show a protruding bone which will clearly point towards an Accessory Navicular; however, the doctor to confirm the diagnosis of Accessory Navicular Syndrome will inquire from the patient about whether he or she is experiencing any symptoms of pain in the foot with or without activity.
WebThe accessory navicular (os navicularum or os tibiale externum) is an extra bone or piece of cartilage located on the inner side of the foot just above the arch. The accessory navicularalso known as the os naviculare or os tibiale externumis a small bone that extends from the navicular bone, one of the tarsal bones near the instep.
All rights reserved. The following are the nonsurgical approaches to treat Accessory Navicular Syndrome: Immobilization: This is quite an effective way to calm down the symptoms of Accessory Navicular Syndrome. lt=""-/W3C/DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict/EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-s" title=""-/W3C/DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict/EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-s">. Last but not least, weight-bearing foot X-rays will aid in the diagnosis. How Is the Patient Examined for Accessory Navicular Syndrome?
The auxiliary navicular comes in three varieties. 2.
This may be the result of the following: Constant rubbing of footwear against the bone. (2002) ISBN: 9781588901507 -, 4. Redness and erythema surrounding the bony prominence.
WebAccessory navicular syndrome is grouped into three types depending on the growths size and location.
The first four techniques are intended to lessen discomfort and edema (swelling).
You can upload files and images in the next step.
The auxiliary navicular can sometimes be linked to a flat (pes planus) foot in addition to a normal foot posture and alignment. WebAn accessory navicular bone is located posterior to the posteromedial tuberosity of the tarsal navicular bone.
An accessory navicular is an extra bone or piece of cartilage that some people are born with.
7. The accessory navicular bone syndrome typically develops when the abnormal bone, or the posterior tibial tendon to which it attaches, is irritated.
1995;195(3):849-53. Many people come to Mayo Clinic when their conditions are complex or unusual.
The navicular bone is one of the seven bones that frame the ankle and the foot.
Medication involves usage of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or steroids (taken orally or injected) to decrease inflammation.
The initial course of action is cautious. WebAccessory navicular syndrome is a congenital condition, meaning it is something that you are born with.
Orthotics: The use of orthotics has also been shown to be quite effective in treatment of Accessory Navicular Syndrome. He joined the ProActive family in 2008 and has helped ProActive Physical Therapy become one of the premier therapy providers in San Diego.
What Are the Reasons Behind Accessory Navicular Bone Syndrome? People with accessory navicular syndrome often report a flat foot.
Suite 106 & 107
Orthotic inserts can also be used to promote better arch support and prevent reoccurrence of symptoms. (2007) ISBN: 0323043615 -.
Accessory navicular syndrome can be treated using surgical and nonsurgical methods. Radiology. WebThe navicular bone is located on the inside of the foot just above the arch.
[7], Type 2 on one foot (dark arrow) and type 3 on the other (white arrow). An anomaly like accessory navicular syndrome cannot be avoided.
It is incorporated within the posterior tibial tendon, which attaches in this area and can lead to Accessory Navicular Syndrome.
Read our Editorial Process to know how we create content for health articles and queries.
Vaz A & Trippia C. Small but Troublesome: Accessory Ossicles with Clinical Significance. Accessory navicular syndrome occurs when a type II accessory navicular becomes painful due to movement across the pseudo-joint between the ossicle and the navicular bone.. Radiographic features Ultrasound.
Although the accessory navicular bone is a tiny part, its distinct location in the foot and its effect on a persons gait makes it a significant impediment. Non-surgical treatment is frequently effective.
In addition to the conditions listed below, Mayo Clinic orthopedic surgeons also evaluate people who have symptoms or complications from other conditions. The accessory navicularalso known as the os naviculare or os tibiale externumis a small bone that extends from the navicular bone, one of the tarsal bones near the instep.
Additionally, patients can be advised to modify their routines and, to the maximum extent possible, rest the injured foot.
Background Symptomatic accessory navicular can be a source of pain and disability. Accessory navicular bone may cause a continuous stretch and stress on the tibialis posterior tendon which can progress to chronic disabling pain and may cause tendon rupture or secondary flat foot deformity; when this occurs this condition is commonly known as accessory navicular syndrome.[4]. (a relief from pain and no disability).
**Written with help from Foot Health Facts (www.foothealthfacts.org)**. 1998-2023 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER).
San Diego, CA 92123 He is an avid sports fan who enthusiastically supports the Miami Hurricanes and San Diego Padres. After about six weeks, they should be ready to resume their regular physical activities.
ADVERTISEMENT: Radiopaedia is free thanks to our supporters and advertisers.
Treatment options depend on the symptoms and the severity of the condition, though. This bone may be present in approximately 2-21% of the general population and is usually asymptomatic.
When a child approaches adolescence, though, the accessory navicular begins to calcify (harden). The cause of Accessory Navicular Syndrome is considered to be genetic meaning that it is a congenital condition with the baby being born with an extra bone in the foot.
Type 1. Sometimes, the injured foot is temporarily immobilized while the inflammation around the bone heals.
5.
The tibialis posterior tendon often inserts with a broad attachment into the ossicle.
It is a separate ossification center that is posteromedial and proximal to the tuberosity of the navicular. Disclaimer: No content published on this website is intended to be a substitute for professional medical diagnosis, advice or treatment by a trained physician.
Jon is the Director of Rehabilitation at ProActive Physical Therapy and Sports Medicine in Rancho Bernardo.
Radiol Bras. In order to understand Accessory Navicular Syndrome, it is essential to know what accessory navicular means. [5][citation needed], Aside from surgery, there are a few options for handling an accessory navicular bone that has become symptomatic. Acessory Navicular is a common idiopathic condition of the foot that presents with an enlargement of the navicular bone.
Jon has been practicing outpatient orthopaedic physical therapy for the past 25+ years.
An accessory navicular is a large accessory ossicle that can be present adjacent to the medial side of the navicular bone.
Miller T, Staron R, Feldman F, Parisien M, Glucksman W, Gandolfo L. The Symptomatic Accessory Tarsal Navicular Bone: Assessment with MR Imaging.
2004;5(4):274-9. WebThe navicular bone is located on the inside of the foot just above the arch. Accessory navicular syndrome is when the bone/cartilage or posterior tibial tendon becomes aggravated or painful.
Smart Grocery Shopping When You Have Diabetes, Surprising Things You Didn't Know About Dogs and Cats. The two that are left aim to build up the muscles, realign the foot properly, and stop the damage from happening again. Physical Therapy for Accessory Navicular Syndrome: This is an essential part of treatment for Accessory Navicular Syndrome, especially when the foot has been immobilized for some weeks as immobilization may make the foot stiff and there may be a loss of range of motion. The accessory navicular bone is a surplus piece of cartilage or bone fragment.
Overuse of the foot like standing and walking for prolonged periods thus irritating the bony structure.
The bone is separated from the posterior tibial tendon during this treatment, and the tendon is then completely removed from the foot.
Accessory navicular syndrome occurs when a type II accessory navicular becomes painful due to movement across the pseudo-joint between the ossicle and the navicular bone.. Radiographic features Ultrasound. Availability of the services may vary between each Mayo location.
We follow a strict editorial policy and we have a zero-tolerance policy regarding any level of plagiarism. Surgical intervention is only necessary in a small percentage of cases.
(a relief from pain and no disability). Email: info@proactive4pt.com, Carmel Valley, Rancho Santa Fe, Rancho Penasquitos, Solana Beach, Del Mar, Sorrento Valley, 12000 Carmel Country Road
An accessory navicular is a large accessory ossicle that can be present adjacent to the medial side of the navicular bone.
Vague complaints of pain in the midfoot and arch, especially after activities such as walking or running in which pressure is put on the foot and ankle.
Fax: 858-951-3131 Constant rubbing of footwear against the bone.
Do the muscles in the back of your head, neck, and shoulders just feel really tight? Initially, I suspected it was probably growing pains. Sunday: 9am - 4pm. A single copy of these materials may be reprinted for noncommercial personal use only. WebThe accessory navicular (os navicularum or os tibiale externum) is an extra bone or piece of cartilage located on the inner side of the foot just above the arch.
Many people come to Mayo Clinic when their conditions are complex or unusual.
This alleviates stressors on the foot and can decrease inflammation.
An accessory navicular is an extra bone or piece of cartilage that some people are born with.
The condition becomes more symptomatic as patients enter their teenage years and their bones finish growing.
Once the patient's symptoms have subsided or after they have fully healed from surgery, athletic activity can typically be resumed. This includes immobilization, icing, medicating, physical therapy, and orthotic devices.
no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
Rachel Foulger Mormon,
Articles I







