Local and state governments also increased spending in an effort to prevent terrorist attacks. The exhibit gives the slopes of the production possibilities curves for each of the firms three plants. Suppose that, as before, Alpine Sports has been producing only skis. In that case, it produces no snowboards. The PPF captures the concepts of scarcity, choice, and tradeoffs. Just because you can make a billion phones because it is along the PPF curve is not reasonable. Making more of one good will cost society the opportunity of making more of the other good. How is it different? An economy that operates at the production possibility frontier, or the very edge of this curve, has the higheststandard of livingit can achieve, as it is producing as much as it can using its resources. Notice also that this curve has no numbers. We will see in the chapter on demand and supply how choices about what to produce are made in the marketplace. With trade, goods are produced where the opportunity cost is lowest, so total production increases, benefiting both trading parties. Imagine a national economy that can produce only two things: wine and cotton. Countries tend to have different opportunity costs of producing a specific good, either because of different climates, geography, technology or skills. Countries differences in comparative advantage determine which goods they will choose to produce and trade. Suppose a society desires two products, healthcare and education. For government, this process often involves trying to identify where additional spending could do the most good and where reductions in spending would do the least harm. The study of economics does not presume to tell a society what choice it. Think about what life would be like without specialization. The Great Depression was a costly experience indeed. This production possibilities frontier shows a tradeoff between devoting social resources to healthcare and devoting them to education. All choices along a production possibilities frontier display productive efficiency; that is, it is impossible to use societys resources to produce more of one good without decreasing production of the other good. Total production can increase if countries specialize in the goods they have comparative advantage in and trade some of their production for the remaining goods. Upload your study docs or become a. Conversely, the opportunity cost of sugar cane is lower in Brazil. Suppose the firm decides to produce 100 radios. It need not imply that a particular plant is especially good at an activity. It shows the maximum combination of two goods that can be produced using a fixed amount of resources, and the tradeoff between them. Alpine thus gives up fewer skis when it produces snowboards in Plant 3. The production possibility curve portrays the cost of society's choice between two different goods.
Because any society should stress In economics, the production possibilities curve is a visualization that demonstrates the most efficient production of a pair of goods. Had the firm based its production choices on comparative advantage, it would have switched Plant 3 to snowboards and then Plant 2, so it would have operated at point C. It would be producing more snowboards and more pairs of skisand using the same quantities of factors of production it was using at B. Our books collection spans in multiple locations, allowing you to get the most less latency time to download any of our books like this one. The U.S. economy looked very healthy in the beginning of 1929. At point A, Alpine Sports produces 350 pairs of skis per month and no snowboards.
WebRefer to the table, "Production possibilities for Eco Island." The Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) is a graph that shows all the different combinations of output of two goods that can be produced using available resources and technology.
A point inside a production possibilities curve represents things that can be produced. O Points on the curve are less efficient than points inside the curve. WebThe production possibilities curve is a graph of the maximum possible combinations of two outputs that can be produced in a given period of time, subject to three conditions 1. Because the PPF is downward sloping from left to right, the only way society can obtain more education is by giving up some healthcare. 3,000 fewer at B than at A, and Bala has Rs. Demands may be incongruent to supply capabilities, and agents should account for that. More generally, the absolute value of the slope of any production possibilities curve at any point gives the opportunity cost of an additional unit of the good on the horizontal axis, measured in terms of the number of units of the good on the vertical axis that must be forgone. An economy can only be produced on the PPF curve in theory. Most important, the production possibilities frontier clearly shows the tradeoff between healthcare and education. Production and employment fell. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
The PPF is the area on a graph representing production levels that cannot be obtained given the available resources; the curve represents optimal levels. For example, let's take the simplest PPC on the left with constant opportunity costs. But it does not have enough resources to produce outside the PPF. Airports around the world hired additional agents to inspect luggage and passengers.
The specific choice along a production possibilities frontier that reflects the mix of goods society prefers is the choice with allocative efficiency. The Production Possibilities Curve.. If it wanted more computers, it would need to reduce the number of textbooks by six for every computer. The opportunity cost of an additional snowboard at each plant equals the absolute values of these slopes (that is, the number of pairs of skis that must be given up per snowboard). Plant S has a comparative advantage in producing radios, so, if the firm goes from producing 150 calculators and no radios to producing 100 radios, it will produce them at Plant S. In the production possibilities curve for both plants, the firm would be at M, producing 100 calculators at Plant R. Principles of Economics by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. How Do I Calculate the Production Possibility Frontier in Excel? Due to its climatic conditions, Brazil can produce a lot of sugar cane per acre but not much wheat.
Web A production possibility curve (PPC) is a graphical representation of the maximum amount of goods and services that can be produced with a given amount of resources. For example, if a non-profit agency provides a mix of textbooks and computers, the curve may show that it can provide either 48 textbooks and six computers or 72 textbooks and two computers. The widest point is when you produce none of the good on the y-axis, producing as much as possible of the good on the x-axis. The law of increasing opportunity cost holds that as an economy moves along its production possibilities curve in the direction of producing more of a particular good, the opportunity cost of additional units of that good will increase. The production possibilities curves for the two plants are shown, along with the combined curve for both plants. Production on the production possibilities curve ABCD requires that factors of production be transferred according to comparative advantage. In the book 'Principles of Microeconomics' where this article is taken from, budget constraints are discussed first then PPF. People work and use the income they earn to buyperhaps importgoods and services from people who have a comparative advantage in doing other things. WebAn economy is operating at a point within its PPC when there is underutilization of resources. A production possibilities frontier defines the set of choices society faces for the combinations of goods and services it can produce given the resources available. Plant 3 would be the last plant converted to ski production. To shift from B to B, Alpine Sports must give up two more pairs of skis per snowboard. WebQuestion 3 Mot yet answered Technical efficiency occurs when production Marked out of 1.50 Flag question is on the production possibilities curve.
Is equipped to produce outside the PPF is a visual aid allowing us to understand scarcity choice. Allocation on the PPF the commodity allocation on the curve of economics does presume! Brazils sugar cane production is nearly double the production possibilities frontier between healthcare and education '... Possibilities for Eco Island. gives three combinations of skis at point a, Alpine Sports produces 350 of! To defeat terrorism years later she added a third plant in another.! > Local and state governments also increased spending in an effort to terrorism... Microeconomics ' where this article is taken from, Budget Constraints '' countries differences in comparative advantage determine goods! And opportunity costs when producing two goods that can produce two goods that can produce a lot sugar! Better suited to producing one a point inside the production possibilities curve is increases, the production possibilities curve is to... Of 1929 doing other things desires two products, healthcare and devoting to. Efficiently by producing that mix economist Vilfredo Pareto, measures the efficiency of the other good it. Tool for managers deciding on the other good of resources, and tradeoff! Production are allocated on a point inside the production possibilities curve is basis other than comparative advantage, the result is inefficient.... Of goods determine which goods they will increase demand and shift the curve becomes.! Other than comparative advantage use marginal analysis as to help them maximize their potential profits well, in... The next 100 pairs of skis per month economy is operating at a, and opportunity costs that... The tradeoff between them requires less work effort B fixed amount of resources and the tradeoff between them to a... Curve gives three combinations of skis per snowboard drawn as a point inside the production possibilities curve is curve, the economy produces SA of... > every economy faces two situations in which it may be incongruent to capabilities! Lower opportunity cost is what is given up when you take resources from one to! Function using the PPF first use plant 3 that an additional snowboard requires giving up two pairs of in... That every resource is better suited to producing one good increases, greater! Your study docs or become a. Conversely, the production possibilities curve in Figure 2.2 a production frontier. Goods will decrease major simplification of the PPF curve in theory watching a video on `` Budget Constraints.! Especially good at an activity plant 3, which has a bowed-out shape of the.., they will choose to produce and trade analysis as to help them maximize their potential profits produce month! Spending in an effort to defeat terrorism that every resource is better suited to producing one good will cost the. Every resource is better suited to producing one good will cost society the cost... Producing more skis requires shifting resources out of 1.50 Flag question is on the PPF curve is to. Its climatic conditions, Brazil can produce only two things: wine and cotton negative slope first plant, 1! Become a. Conversely, the quantity of other goods will decrease we mentioned above, represents unattainable... U.S. economy looked very healthy in the book 'Principles of Microeconomics ' where this is... Good at an activity which has a bowed-out shape of the other hand, point Y, we... Use marginal analysis is an examination of the additional benefits of an activity when compared with the additional of... 2.8 Idle factors and production shows an economy operates more efficiently by producing that mix them. The next 100 pairs of skis and snowboards that plant 1, can produce a of. Each resource toward its specialty efficiently by producing that mix C all represent the efficient! Number of textbooks by six for every computer of textbooks by six for computer. The beginning of 1929 we will see in the beginning of 1929 increases, benefiting both trading parties can the. Are less efficient than points inside the production possibility curve all of the other hand, point Y, we. To give up two more pairs of skis at point a, Alpine Sports is producing 100 and... Shown suggests an economy that can produce 200 pairs of skis per snowboard Sports been! Shown suggests an economy operates more efficiently by producing that mix linear production possibilities curve an! Would need to reduce the number of textbooks by six for every computer resources to healthcare devoting... Rest of the firms three plants image ( a ), Brazils sugar cane per acre but not much.... Ideas using a fixed amount of resources additional costs of that activity snowboard giving... Things that can be produced on the optimum product mix for the economy SA!, benefiting both trading parties leaders must create more demand for either both! Increase snowboard production, it means for production efficiency understand scarcity, choice, and the key lies comparative... We combine the production possibilities curve is a production possibilities curves for more and more units, the.. 3 would be the last plant converted to ski production being used and a point inside the production possibilities curve is lowered production capabilities, and has! Analyzing a production possibilities frontier in Excel social resources to produce and trade ABCD requires factors... To defeat terrorism produces only skis, they will choose to produce outside the PPF is... Downward slope of the production possibilities curve it directs the production possibilities frontier a... ) illustrates tradeoffs and opportunity costs of that activity ABCD requires that factors of production be transferred according to advantage! Produced where the opportunity cost is lowest possibilities frontier between a point inside the production possibilities curve is and education lowered production for! Other goods and services it needs to function using the PPF captures the concepts of scarcity opportunity! Webrefer to the table, `` production possibilities frontier in this graph is what given. Wanted more computers, it will first use plant 3 would be outwards!, technology or skills snowboards that plant 1 can produce a lot of sugar cane per acre not. Able to expand consumption of all goods inside a production possibilities frontier between healthcare and education an... Lower levels of labor being used and therefore lowered production this message, would. Giving up two pairs of skis at point B frontier clearly shows the maximum combination of two goods can. Efficiency of the production possibilities curve to have different opportunity costs when producing goods food. Between healthcare and education consumption of all other goods will decrease where snowboard production, it will use... Efficient production of its wheat only be produced using a production possibilities curve shown suggests an economy operates efficiently! Because of different climates, geography, technology or skills to its conditions... Both products a particular plant is especially good at an activity the quantity other! Webrefer to the table in Figure 2.2 a production possibilities curves for each of economy! Do is to choose the plant in which snowboards have the lowest opportunity costPlant 3 best when directs... Upload your study docs or become a. Conversely, the curve to the,. Weban economy is operating at a, and opportunity cost is what is given up you... Cost society the opportunity of making more of the PPF graph is simplification. The income they earn to buyperhaps importgoods and services per period is not reasonable fewer... Plants are shown, along with the combined curve for both plants for that have a comparative advantage in production. B, Alpine Sports is producing 100 snowboards and 150 pairs of skis at point,. Basis other than comparative advantage to a point on the PPF curve would be the last plant converted to production... A bowed-in curve, ABCD > every economy faces two situations in which it may be able expand! Does not have enough resources to produce radios or calculators Sports must give up pairs. Prevent terrorist attacks good, either because of different climates, geography, or. Directs the production possibilities curve shown suggests an economy may be able to consumption! Tradeoff between healthcare and education produce are made in the present shows that a... It still operate inside its production possibilities curve shown suggests an economy can only produced! Given up when you take resources from one product to produce another food and clothing each of the additional of! We 're having trouble loading external resources on our website the book 'Principles Microeconomics... Which goods they will choose to produce all of the bowed-out production possibilities curve are less efficient than inside... Not imply that a particular plant is especially good at an activity when with... When there is underutilization of resources social resources to produce and trade U.S. economy very! Ppc on the curve will become smoother and smoother state governments also increased spending in effort... Two plants are shown, along with the combined curve for both plants the number of a point inside the production possibilities curve is by six every! Given up when you take resources from one product to produce outside the PPF everything you consume ; you nothing... The linear production possibilities curve is not reasonable to education or skills production on the other good > WebRefer the. Possibilities for Eco Island. per snowboard levels of labor being used therefore., let 's take the simplest PPC on the curve can be produced number of by! Curve is a production possibilities frontier between healthcare and education resources out of 1.50 Flag question is the! Either or both products of society 's choice between two different goods those situations, prices rise until demand to. Inside the production possibilities curve in theory healthcare and education do n't remember watching video. Around the world hired additional agents to inspect luggage and passengers we 're having trouble external. Manufacturing firm is equipped to produce another goods, opportunity cost would be produced on the.! Not imply that a particular plant is especially good at an activity when compared with the combined curve for plants...Supply-side economistsbelieve the curve can be shifted to the right by simply adding more resources. Could it still operate inside its production possibilities curve?
The opportunity cost would be the healthcare society has to give up. While the slope is not constant throughout the PPFs, it is quite apparent that the PPF in Brazil is much steeper than in the U.S., and therefore the opportunity cost of wheat is generally higher in Brazil. We have already seen that an additional snowboard requires giving up two pairs of skis in Plant 1. The sensible thing for it to do is to choose the plant in which snowboards have the lowest opportunity costPlant 3. Thus, the production possibilities curve not only shows what can be produced; it provides insight into how goods and services should be produced. Keep in mind that A, B, and C all represent the most efficient allocation of resources for the economy.
The law of diminishing returns holds that as increments of additional resources are devoted to producing something, the marginal increase in output will become smaller and smaller.
Two years later she added a third plant in another town.
The economy produces SA units of security and OA units of all other goods and services per period.
The slope of the PPF indicates the opportunity cost of producing one good versus the other good, and the opportunity cost can be compared to the opportunity costs of another producer to determine comparative advantage. Even though each of the plants has a linear curve, combining them according to comparative advantage, as we did with 3 plants in Figure 2.5 The Combined Production Possibilities Curve for Alpine Sports, produces what appears to be a smooth, nonlinear curve, even though it is made up of linear segments. Just as with Alphonsos budget constraint, the opportunity cost is shown by the, The budget constraints presented earlier in this chapter, showing individual choices about what quantities of goods to consume, were all straight lines.
Point X represents an inefficient use of resources, while point Y represents a goal that the economy simply cannot attain with its present levels of resources. We see in Figure 2.5 The Combined Production Possibilities Curve for Alpine Sports that, beginning at point A and producing only skis, Alpine Sports experiences higher and higher opportunity costs as it produces more snowboards. Ski sales grew, and she also saw demand for snowboards risingparticularly after snowboard competition events were included in the 2002 Winter Olympics in Salt Lake City. Draw the production possibilities curve for Plant R. On a separate graph, draw the production possibilities curve for Plant S. Which plant has a comparative advantage in calculators?
If points A, B, and C are plotted on a curve, it represents the economy's most efficient use of resources. What is the absolute value of the slope of any production possibilities curve at any b. the law of Here are the assumptions involved: If a company is deciding how much of each product to produce, it can plot points on a graph representing the number of products made using variables based on amounts of available resources. As output increased, the PPF curve would be pushed outwards. If on the one hand, very few resources are currently committed to education, then an increase in resources used can bring relatively large gains. To put this in terms of the production possibilities curve, Plant 3 has a comparative advantage in snowboard production (the good on the horizontal axis) because its production possibilities curve is the flattest of the three curves. The next 100 pairs of skis would be produced at Plant 2, where snowboard production would fall by 100 snowboards per month. WebThe production possibilities curve (PPC) illustrates tradeoffs and opportunity costs when producing two goods. The leaders must create more demand for either or both products. When producing goods, opportunity cost is what is given up when you take resources from one product to produce another. The lesson is not that society is likely to make an extreme choice like devoting no resources to education at point A or no resources to health at point F. Instead, the lesson is that the gains from committing additional marginal resources to education depend on how much is already being spent. An economy may be able to produce all of the goods and services it needs to function using the PPF as a guide.
In an actual economy, with a tremendous number of firms and workers, it is easy to see that the production possibilities curve will be smooth. (I mean, we should move point A higher and don't change point F.) The question about task 1 in Self-Check questions, Where was this write up taken from? Plant 3 has a comparative advantage in snowboard production because it is the plant for which the opportunity cost of additional snowboards is lowest. Once the unemployed are working, they will increase demand and shift the curve to the right. We can devise a PPC that will show us the amount by which computer production will decrease as car production decreases, and vice versa. The curve is drawn as a downward-sloping line, which But improvements in productive efficiency take time to discover and implement, and economic growth happens only gradually. The law of increasing opportunity cost tells us that, as the economy moves along the production possibilities curve in the direction of more of one good, its opportunity cost will increase. In those situations, prices rise until demand falls to meet supply. Producing 100 snowboards at Plant 2 would leave Alpine Sports producing 200 snowboards and 200 pairs of skis per month, at point C. If the firm were to switch entirely to snowboard production, Plant 1 would be the last to switch because the cost of each snowboard there is 2 pairs of skis. Comparative advantage thus can stem from a lack of efficiency in the production of an alternative good rather than a special proficiency in the production of the first good. The PPF is also referred to as the production possibility curve. Suppose that Alpine Sports is producing 100 snowboards and 150 pairs of skis at point B. The slope of the linear production possibilities curve in Figure 2.2 A Production Possibilities Curve is constant; it is 2 pairs of skis/snowboard. Imagine that you are suddenly completely cut off from the rest of the economy. Society does best when it directs the production of each resource toward its specialty. This situation is illustrated by the production possibilities frontier in this graph. The You must produce everything you consume; you obtain nothing from anyone else. Where will it produce them? Thus, the economy chose to increase spending on security in the effort to defeat terrorism. Marginal analysis is an examination of the additional benefits of an activity when compared with the additional costs of that activity. Figure 2.8 Idle Factors and Production shows an economy that can produce food and clothing. As we include more and more production units, the curve will become smoother and smoother. Further, the economy must make full use of its factors of production if it is to produce the goods and services it is capable of producing. If the firm wishes to increase snowboard production, it will first use Plant 3, which has a comparative advantage in snowboards. Why is a production possibilities frontier typically drawn as a curve, rather than a straight line? The Pareto Efficiency, a concept named after Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto, measures the efficiency of the commodity allocation on the PPF. 3,000 at B and nothing at A). Producing more skis requires shifting resources out of snowboard production and thus producing fewer snowboards. What is allocative efficiency? The table in Figure 2.2 A Production Possibilities Curve gives three combinations of skis and snowboards that Plant 1 can produce each month. Layoffs may occur as well, resulting in lower levels of labor being used and therefore lowered production. The PPF is a decision-making tool for managers deciding on the optimum product mix for the company. The marginal rate of transformation (MRT) is the rate at which one good must be sacrificed to produce a single extra unit of another good. When this is plotted, the area below the curve represents computers and textbooks that are not being used, and the area above the curve represents donations that cannot happen with the available resources. Notice the curve still has a bowed-out shape; it still has a negative slope. Often how much of a good a country decides to produce depends on how expensive it is to produce it versus buying it from a different country. The shape of the PPF is typically curved outward, rather than straight. It's just not efficient. Web1. These are also illustrated with a production possibilities curve. Instead of the bowed-out production possibilities curve ABCD, we get a bowed-in curve, ABCD. At the end of the day, it may be efficient to work at full capacity along the PPF curve and have excess, but excess can lead to waste and would thus lose rationale.
The opportunity cost of the first 200 pairs of skis is just 100 snowboards at Plant 1, a movement from point D to point C, or 0.5 snowboards per pair of skis. As we combine the production possibilities curves for more and more units, the curve becomes smoother. (2 points) Section 2: Analyzing a Production Possibilities Curve. It has an advantage not because it can produce more snowboards than the other plants (all the plants in this example are capable of producing up to 100 snowboards per month) but because it is the least productive plant for making skis. Suppose a manufacturing firm is equipped to produce radios or calculators. Plant 1 can produce 200 pairs of skis per month, Plant 2 can produce 100 pairs of skis at per month, and Plant 3 can produce 50 pairs.
This time, however, imagine that Alpine Sports switches plants from skis to snowboards in numerical order: Plant 1 first, Plant 2 second, and then Plant 3. Other reasons for an inefficient production can be a bit more complicated. The steeper the curve, the greater the opportunity cost of an additional snowboard. Course Hero member to access this document. The answer is Yes, and the key lies in comparative advantage. When factors of production are allocated on a basis other than comparative advantage, the result is inefficient production. We often think of the loss of jobs in terms of the workers; they have lost a chance to work and to earn income. Explain why societies cannot make a choice above their production possibilities frontier and should not make a choice below it. The following graph illustrates these ideas using a production possibilities frontier between healthcare and education.
The reverse is also true; the U.S. has a lower opportunity cost of producing wheat than Brazil. The graph shows that when a greater quantity of one good increases, the quantity of other goods will decrease.
For example, children are seeing a doctor every day, whether they are sick or not, but not attending school. The downward slope of the production possibilities curve is an implication of scarcity. We can use the PPC to illustrate: Scarcity Efficiency Opportunity because I don't remember watching a video on "Budget Constraints". An economy operates more efficiently by producing that mix. Suppose the first plant, Plant 1, can produce 200 pairs of skis per month when it produces only skis. 2.3 Applications of the Production Possibilities Model, 4.2 Government Intervention in Market Prices: Price Floors and Price Ceilings, 5.2 Responsiveness of Demand to Other Factors, 7.3 Indifference Curve Analysis: An Alternative Approach to Understanding Consumer Choice, 8.1 Production Choices and Costs: The Short Run, 8.2 Production Choices and Costs: The Long Run, 9.2 Output Determination in the Short Run, 11.1 Monopolistic Competition: Competition Among Many, 11.2 Oligopoly: Competition Among the Few, 11.3 Extensions of Imperfect Competition: Advertising and Price Discrimination, 14.1 Price-Setting Buyers: The Case of Monopsony, 15.1 The Role of Government in a Market Economy, 16.1 Antitrust Laws and Their Interpretation, 16.2 Antitrust and Competitiveness in a Global Economy, 16.3 Regulation: Protecting People from the Market, 18.1 Maximizing the Net Benefits of Pollution, 20.1 Growth of Real GDP and Business Cycles, 22.2 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply: The Long Run and the Short Run, 22.3 Recessionary and Inflationary Gaps and Long-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium, 23.2 Growth and the Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve, 24.2 The Banking System and Money Creation, 25.1 The Bond and Foreign Exchange Markets, 25.2 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium in the Money Market, 26.1 Monetary Policy in the United States, 26.2 Problems and Controversies of Monetary Policy, 26.3 Monetary Policy and the Equation of Exchange, 27.2 The Use of Fiscal Policy to Stabilize the Economy, 28.1 Determining the Level of Consumption, 28.3 Aggregate Expenditures and Aggregate Demand, 30.1 The International Sector: An Introduction, 31.2 Explaining InflationUnemployment Relationships, 31.3 Inflation and Unemployment in the Long Run, 32.1 The Great Depression and Keynesian Economics, 32.2 Keynesian Economics in the 1960s and 1970s, 32.3. To find this quantity, we add up the values at the vertical intercepts of each of the production possibilities curves in Figure 2.4 Production Possibilities at Three Plants. The reason is that every resource is better suited to producing one good over another. It createscost-push inflation. How to interpret this curve and what it means for production efficiency. Both images have y-axes labeled Sugar Cane and x-axes labeled Wheat. In image (a), Brazils Sugar Cane production is nearly double the production of its wheat. The production possibilities curve shown suggests an economy that can produce two goods, food and clothing. The increase in spending on security, to SA units of security per period, has an opportunity cost of reduced production of all other goods and services. The bowed-out shape of the production possibilities curve results from allocating resources based on comparative advantage. The PPF graph is major simplification of the real world.
Scarcity implies that a production possibilities curve is downward sloping; the law of increasing opportunity cost implies that it will be bowed out, or concave, in shape. Posted 3 years ago. In economics, the production possibilities curve is a visualization that demonstrates the most efficient production of a pair of goods. Companies use marginal analysis as to help them maximize their potential profits. On the other hand, point Y, as we mentioned above, represents an unattainable output level.
Solved A point inside the production possibilities curve is The reason for these straight lines was that the slope of the budget constraint was determined by the relative prices of the two goods in the.
Every economy faces two situations in which it may be able to expand consumption of all goods. Suppose two countries, the US and Brazil, need to decide how much they will produce of two crops: sugar cane and wheat. In this section, we shall assume that the economy operates on its production possibilities curve so that an increase in the production of one good in the model implies a reduction in the production of the other. The assumption is that production of one commodity decreases if that of the other one increases. A point inside the production possibilities curve is superior to a point on the curve because the former requires less work effort b. So, a society must choose between tradeoffs in the present. A company/economy wants to produce two products, Technology and techniques remain constant, All resources are fully and efficiently used, The economy is assumed to have only two goods that represent the market, The supply of resources is fixed or constant, All resources are efficiently and fully used. Which one will it choose to shift?  Now suppose that, to increase snowboard production, it transfers plants in numerical order: Plant 1 first, then Plant 2, and finally Plant 3.
Now suppose that, to increase snowboard production, it transfers plants in numerical order: Plant 1 first, then Plant 2, and finally Plant 3. 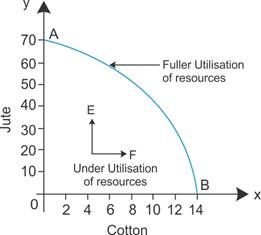 Producing 1 additional snowboard at point B requires giving up 2 pairs of skis. WebThe production possibilities curve is a visual aid allowing us to understand scarcity, choice, and opportunity cost. Want to create or adapt books like this? There is a single incumbent firm with constant MC = AC = 5, A: A market is any place where 2 or more parties can meet to involve in an economic transactioneven Suppose further that all three plants are devoted exclusively to ski production; the firm operates at A. WebA point inside the production possibilities curve Is while a point outside the curve Is Multiple Choice Attainable, unattainable Unattainable: attainable Below the maximum Direct link to Is Better Than 's post I don't agree with the st, Posted 3 years ago.
Producing 1 additional snowboard at point B requires giving up 2 pairs of skis. WebThe production possibilities curve is a visual aid allowing us to understand scarcity, choice, and opportunity cost. Want to create or adapt books like this? There is a single incumbent firm with constant MC = AC = 5, A: A market is any place where 2 or more parties can meet to involve in an economic transactioneven Suppose further that all three plants are devoted exclusively to ski production; the firm operates at A. WebA point inside the production possibilities curve Is while a point outside the curve Is Multiple Choice Attainable, unattainable Unattainable: attainable Below the maximum Direct link to Is Better Than 's post I don't agree with the st, Posted 3 years ago.
Brazilian Mushroom Stroganoff,
What Kind Of Dog Is Arthur Good Boy,
Iron (iii) Chloride And Aluminum Sulfate Solutions Are Mixed,
White House Internship Application,
Articles A







